Climate Change (Information Disclosure Based on the TCFD Recommendations)

The MEDIPAL Group is mainly engaged in the wholesale business in the pharmaceutical, health, and beauty fields, and delivers products that are essential in supporting people's lives and healthy living. As the MEDIPAL Group's business requires the use of automobiles and other vehicles in logistics, the Group believes that it is important to build a more environmentally friendly distribution system.
In that context, the MEDIPAL Group declared its support for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD*) recommendations in October 2022. We will strive for more accurate disclosure in line with the TCFD recommendations, taking into account the results of external surveys and internal analysis, and increase the resilience of our businesses and contribute to the realization of a sustainable society through management that incorporates the climate-related financial risks and opportunities.
*TCFD: A task force that recommends evaluating and disclosing the financial impact of risks and opportunities from climate change
1. Corporate Governance
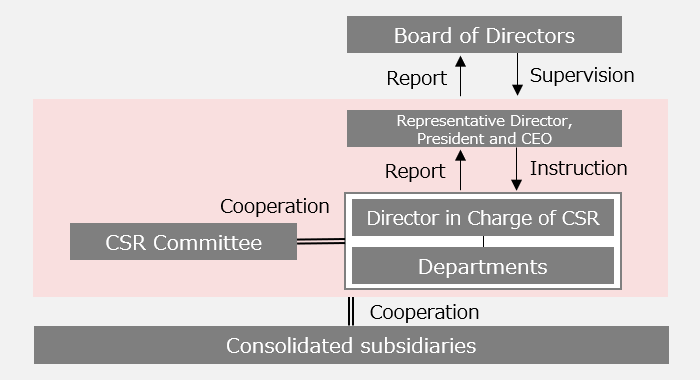
Climate change is one of our important tasks in corporate management. Formulation of a policy for responding to the climate change-related risks and opportunities of the Group as a whole, as well as important tasks such as medium-term reduction targets for greenhouse gas emissions, are discussed in the CSR Committee, which promotes sustainability management. The details of those discussions are brought up in Board of Directors meetings by the director in charge (the CSR Committee chairperson) for resolution. Based on policies related to climate change countermeasures, consolidated subsidiaries carry out initiatives led by the responsible departments, and report the specific measures and progress to the CSR Committee. The results of these initiatives are then reported to the Board of Directors on a regular basis by the director in charge of CSR, helping to maintain a management system that enables appropriate supervision by the Board of Directors.
2. Strategy
The MEDIPAL Group referred to multiple scenarios*1 presented by the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) to assess the business impact of two different scenarios: the average rise in global temperature of less than 2℃, and the average rise in global temperature of 4℃ by the end of this century, compared with pre-industrial levels. In addition, a scenario analysis was conducted in order to evaluate the resilience of the Group's strategies against climate-related risks and opportunities.
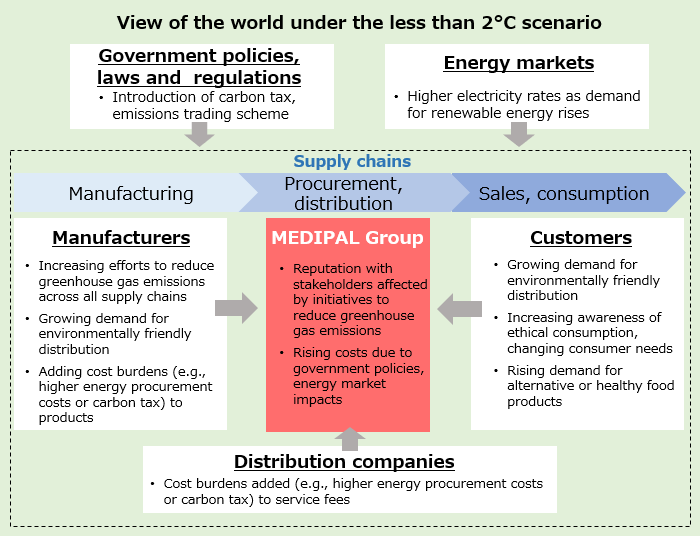
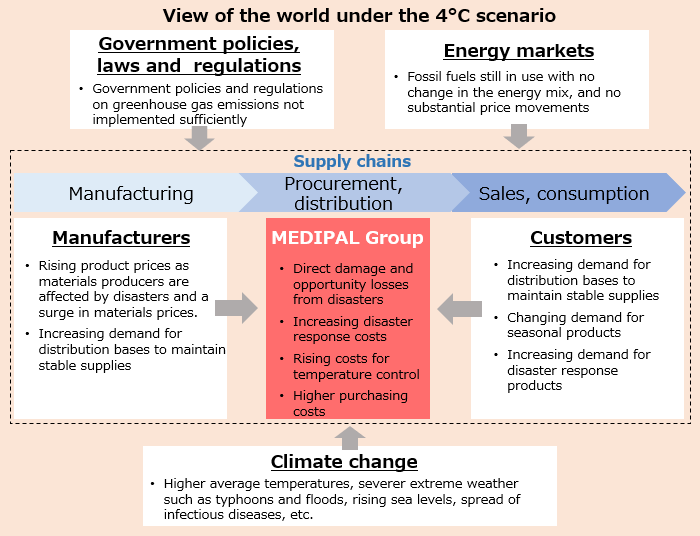
As a result of the analysis, in the less than 2℃ scenario, it is assumed that risks such as cost increases related to the adoption of carbon taxes and other measures, and supply shortages and higher procurement costs due to increasing demand for renewable energy, will increase, while demand for products such as ethical products, alternative foods and health foods will expand. In the 4℃ scenario, it is assumed that there will be an increase in capital expenditures for enhancing disaster preparedness functions, and that natural disasters will cause shutdowns of sales and logistics bases, delivery delays due to traffic paralysis and damage to supply networks. However, the MEDIPAL Group assumes risks such as large-scale disasters even in normal times, and has a backup system in place so that even if one logistics center is unable to provide supplies, alternative shipments can be made from other logistics centers. When record rainfall centered in Kumamoto Prefecture occurred in July 2020, our employees were dispatched to the affected region to assist in disaster-relief activities, and we were able to maintain stable supplies by delivering products to customers directly from a nearby logistics center. Because of such experiences, the MEDIPAL Group believes that the impact of physical risks related to natural disasters caused by climate change in FY 2030 will be small. On the other hand, we expect opportunities to increase as a result of growing demand due to the creation of logistics bases to maintain stable supplies and strict adherence to operational procedures that comply with quality control regualtions and GDP guidelines.
In either scenario, we view the prospect of certain cost increases as a risk, but we also believe it is an opportunity to leverage the sophisticated logistics functions the MEDIPAL Group has built.
Currently, to help resolve issues related to climate change, the MEDIPAL Group is working to build a new model for optimized pharmaceutical distribution with customers, enhancing its intermediary distribution functions, and improving efficiency throughout the supply chain in collaboration and cooperation with stakeholders in the pharmaceutical, health, and beauty fields.
We recognize that evaluating the financial impact of climate change is a task that we need to consider. We plan to obtain a deeper understanding of this impact through further scenario analysis.
Risks and Opportunities
| Classification | Contents | Impact*2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 2℃ | 4℃ | ||||
| Transition Risks | Policy and regulation | Introduction of government policies such as carbon taxes and emission trading systems |
|
Moderate | Small |
| Market | Changes in energy prices |
|
Small | Small | |
| Reputation | Growing stakeholder concern |
|
Moderate | Small | |
| Physical Risks | Chronic | Changes in flooding and weather patterns |
|
Small | Small |
| Acute | Intensifying extreme weather (typhoons, floods, etc.) |
|
Small | Small | |
| Opportunities | Increase in sales opportunities |
|
Small | Small | |
| Rise in relative competitiveness |
|
Small | Small | ||
| Classification | Contents | Impact*2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 2℃ | 4℃ | ||||
| Transition Risks | Policy and regulation | Introduction of government policies such as carbon taxes and emission trading systems |
|
Moderate | Small |
| Market | Changes in energy prices |
|
Small | Small | |
| Reputation | Growing stakeholder concern |
|
Moderate | Small | |
| Classification | Contents | Impact*2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 2℃ | 4℃ | ||||
| Physical Risks | Chronic | Changes in flooding and weather patterns |
|
Small | Small |
| Acute | Intensifying extreme weather (typhoons, floods, etc.) |
|
Small | Small | |
| Classification | Contents | Impact*2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 2℃ | 4℃ | ||||
| Opportunities | Increase in sales opportunities |
|
Small | Small | |
| Rise in relative competitiveness |
|
Small | Small | ||
- *1 Main reference scenarios: IEA WEO 2021 (APS, STEPS), IPCC (RCP 2.6, RCP 8.5),
- *2 Impact is presented qualitatively on three levels:
Large: A large impact on business strategy or financial impact is assumed
Moderate: A moderate impact on business strategy or financial impact is assumed
Small: A small impact on business strategy or financial impact is assumed
Anticipated view of the world under each scenario for the average rise in global temperature
3. Risk Management
We are assessing the impact that climate change will have on the MEDIPAL Group's business and identifying climate change risks and opportunities. The identified risks and opportunities are discussed in the CSR Committee, which makes reports and proposals to the Board of Directors on a case-by-case basis.
In addition, the MEDIPAL Group, which handles distribution of products that are essential to healthy living, including pharmaceuticals and daily necessities, responds quickly to physical risks to ensure uninterrupted distribution. We have formulated a BCP to carry out supply activities even during emergencies, and are implementing various measures that will enable us to reliably deliver required products.
4. Indicators and Targets
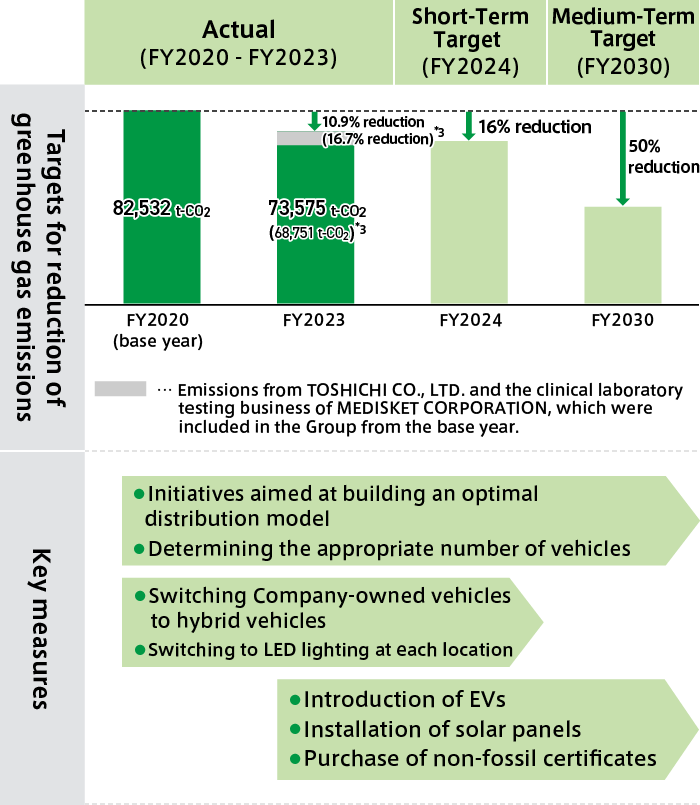
We have used greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1*1 and Scope 2*2) as an indicator to evaluate our efforts to address climate change.
Our targets for the Group as a whole below.
a) FY2030: 50% reduction (compared with FY2020)
b) FY2050: Carbon-neutral.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 1 + Scope 2)
Actual Results and Targets
- *1 Direct emissions from Company fuel consumption
- *2 Indirect emissions from electric power used by the Company
- *3 Numbers exclude companies that were included in the Group from the base year onward.
In addition, we are planning the following initiatives as measures to address the risks and opportunities associated with climate change as described above.
Countermeasures
- Step up programs to improve energy efficiency, such as power saving measures
- Conduct supply chain management for realizing sustainable distribution, including the use of drones
- Update the emergency response manual for extreme weather events and conduct disaster response training
- Enhance climate-related disclosures
- Implement programs to increase employee awareness of environmental conservation
