Activities Report / InformationREPORT & INFORMATION
2025.06.02
Medical and disease information
- #Lysosomal storage diseases
- #Overview
- #Treatment
Basic Knowledge of Lysosomal Storage Diseases-Treatment
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are a group of disorders caused by the dysfunction of lysosomes, leading to the accumulation of unwanted substances in the body. This article explains the main treatments for LSDs.
Related Article: Basic Knowledge of Lysosomal Storage Diseases-Overview
Diagram of Main Treatment Methods
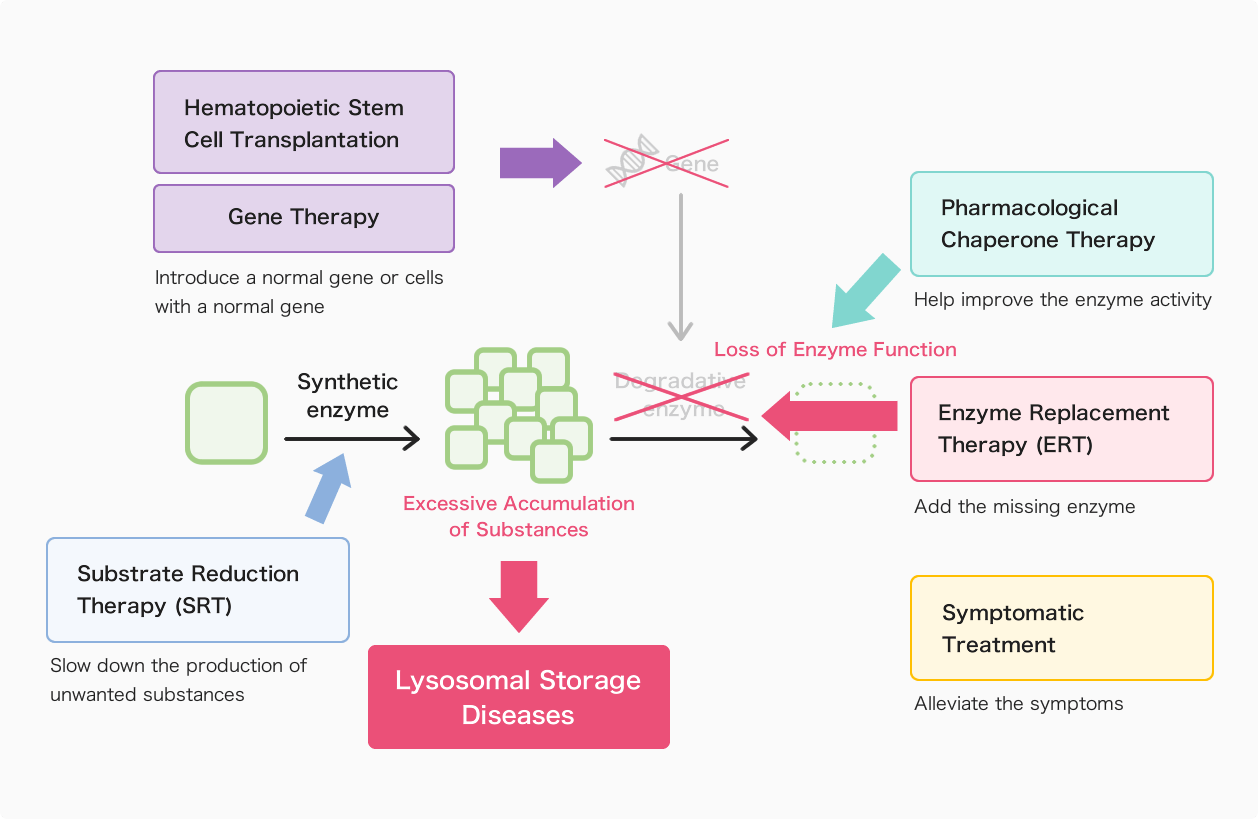






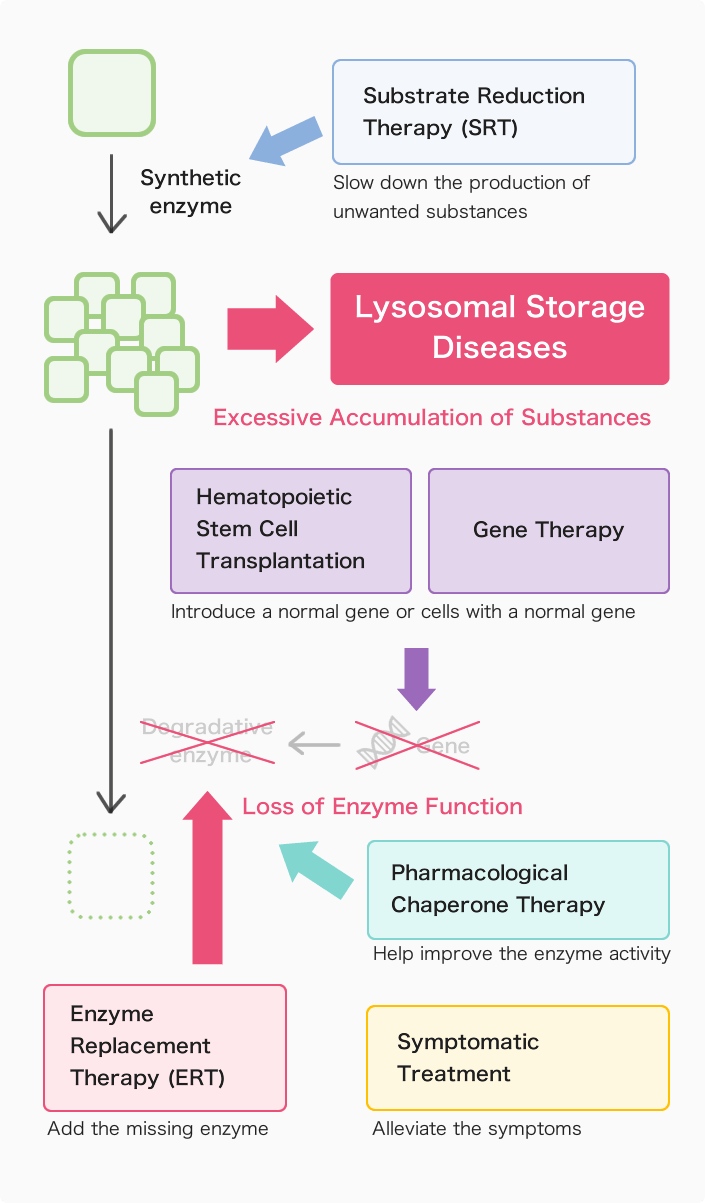






1. Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT)
Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) is a treatment that adds the missing enzyme in the body through regular intravenous (IV) infusions.
Since enzymes are proteins, they would be broken down in the stomach if taken by mouth. Therefore, the medication is given directly into the bloodstream through injections. ERT requires regular infusions, usually once a week or every two weeks.
The medication is administered slowly during the infusions to avoid side effects, such as allergic reactions. So, each session can take several hours.
As of June 2025, ERT is approved for the following LSDs:
- Gaucher disease
- Fabry disease
- Pompe disease
- Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I
- Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II
- Mucopolysaccharidosis Type IVA
- Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VI
- Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VII
- Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency
- Acid sphingomyelinase deficiency
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis Type 2
In recent years, new therapies have been developed for certain LSDs that can be given directly into the brain ventricles or use new technologies to deliver medications to the brain. These treatments expand the options for central nervous system symptoms that traditional ERT cannot address.
2. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) is a treatment that transplants hematopoietic stem cells from a donor, which are the precursors of blood cells.
The transplanted cells develop into cells that produce normal lysosomal enzymes within the patient’s body. These enzymes are thought to help break down the accumulated unwanted substances in the patient’s cells.
HSCT is carried out as one of the standard treatments for certain LSDs because it can provide long-term benefits when successful.
3. Substrate Reduction Therapy (SRT)
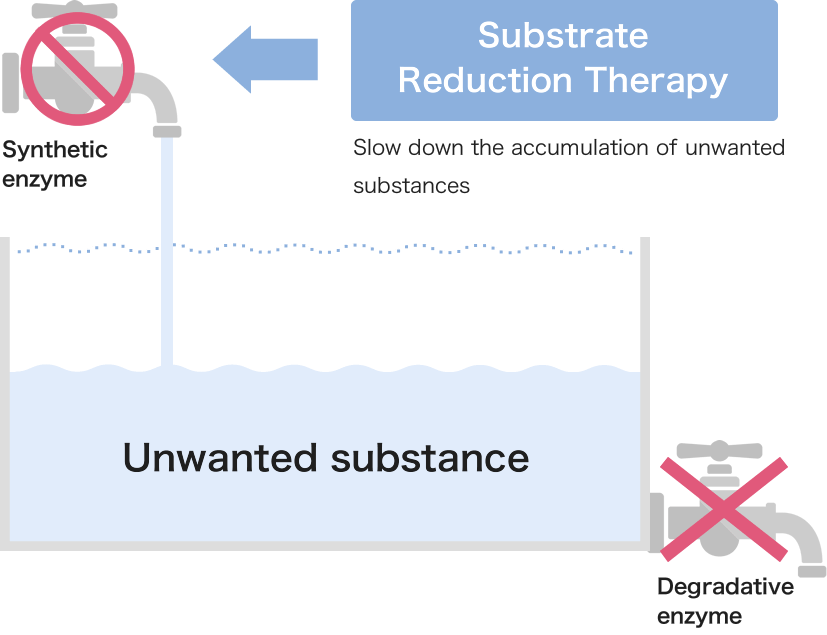
Substrate Reduction Therapy (SRT) is a treatment that slows down the production of substances that cause LSDs, making it harder for unwanted substances to accumulate in the body.
Currently approved SRTs are oral medications taken daily to manage symptoms.
4. Pharmacological Chaperone Therapy
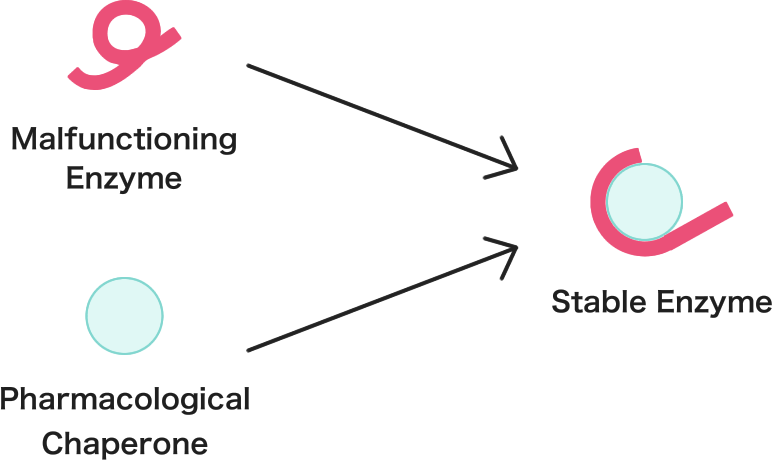
Pharmacological Chaperone Therapy is a treatment that stabilizes the structure of malfunctioning enzymes using small molecules, which helps improve their activity.
Proteins, like enzymes, need to have a proper three-dimensional structure to function correctly. If genetic mutations prevent this, the enzyme cannot work properly.
Pharmacological chaperones support enzymes in achieving this correct structure, enabling them to function.
Since the effectiveness of pharmacological chaperone therapy depends on the specific genetic mutation, it is necessary to confirm the type of gene mutation in the patient before treatment.
5. Gene Therapy
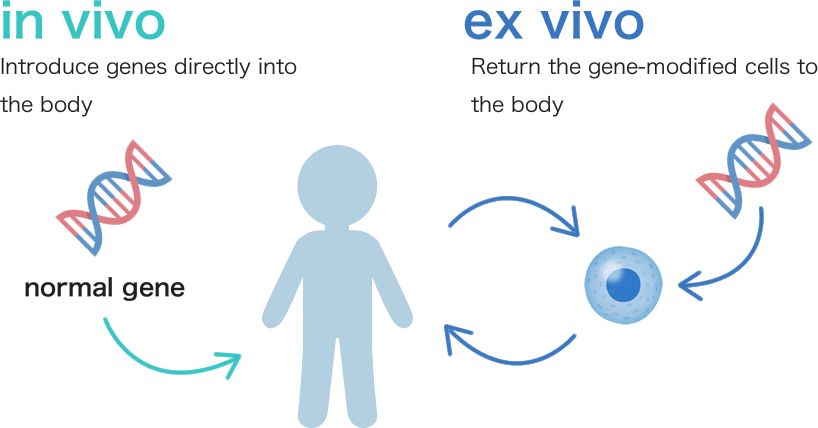
Gene therapy is a treatment that introduces normal genes into the patient’s body to correct the genetic changes that cause the disease. As of June 2025, gene therapy for LSDs has not yet been approved in Japan, but some gene therapies have been approved for certain LSDs in other countries.
There are two main types of gene therapy. “In vivo” gene therapy is given directly into the patient’s body, while “ex vivo” gene therapy introduces the therapeutic gene into cells taken from the patient and then returns those cells back to the body.
6. Symptomatic Treatment
Symptomatic treatment is a method that helps to alleviate the symptoms caused by the disease. For example, anti-epileptic medications can help control seizures, and antihypertensive medications can reduce the strain on the heart and kidneys.
In addition to medications, other treatments such as surgery, dietary therapy, and lifestyle adjustments are also used to help ease the patient’s symptoms as much as possible.
Editorial supervision: Kimitoshi Nakamura, MD, PhD (Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Graduate
School of Medical Sciences, Kumamoto University)
Reference materials
- Yoshikatsu Eto edition. Lysosomal Storage Disease - Recent Advances in Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment - Revised 2nd Edition. SHINDAN TO CHIRYO SHA, Inc. 2023.